| Function type | Instantaneous velocity is a function of layer isopach. |
| Definition of parameters |
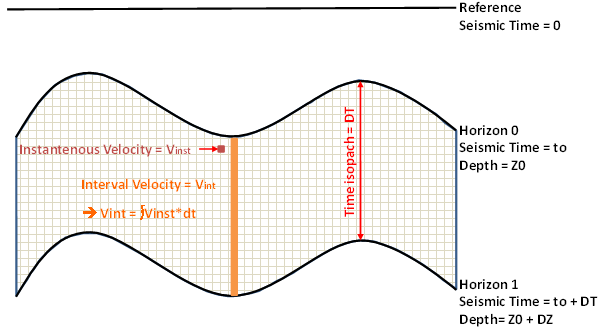
V0 = constant velocity factor (instantaneous velocity at the top of the considered layer). k = constant compaction factor. Z0= depth of the top of the considered layer. |
| Operational applications |
Same as V0 + k × Z, except that V0 is linked to the top of the considered layer. Useful when you are in a layered model and the V0 at reference datum does not reflect a possible change of V0 values at the top of the layer. For example, when there is an important dip effect at the top of the layer. |
$$
V_{inst} = V0 + k \times (Z-Z0)
$$
\( \Rightarrow \) Hypothesis 1: \( Z = Z(t)\)
$$
\Rightarrow V_{inst}(t)=V_0+k \times (Z(t)-Z0)
$$
\(
\Rightarrow \frac{DZ(t)}{dt} = (V0 – k \times Z0) +k \times Z(t) \equiv
\)
first order differential equation
\( \Rightarrow \) General solution \( Z(t) = Ce^{kt}- \frac{V0}{k} + Z0 \)
With \( Z(t_0) = Z0 = Ce^{kt_0} – \frac{V0}{k} + Z0 \Rightarrow C = \frac{V0}{k} e^{-kt_0} \)
\(
Z(t) = \frac{V0}{k} \left( e^{k(t-t_0)} – 1 \right) + Z0 \quad \)
&
\( \quad V_{inst} = V0e^{k(t-t_0)} \)
$$
\boldsymbol{
DZ = \int_{t_0}^{t_0+DT} V_{inst}dt = \int_{t_0}^{t_0+DT} V0 \times e^{k(t-t_0)} dt
}
$$
$$
\boldsymbol{
DZ= \frac{V0}{k} \times \left( e^{kDT} – 1 \right)
}
$$
$$
\boldsymbol{
V_{int}= \frac{V0}{k \times DT} \times \left( e^{kDT} – 1 \right)
}
$$