| Function type |
Approximation of V0+KZ in multi-layer context. Equivalent to V0+KZ if use for first layer, less sensitive to shallower conversion if deeper. |
| Definition of parameters |
V0 = constant velocity factor (instantaneous velocity at the surface). K = constant compaction factor. |
| Operational applications | Useful when geology presents linear compaction (often confirmed by measurements at least in clastic environments). |
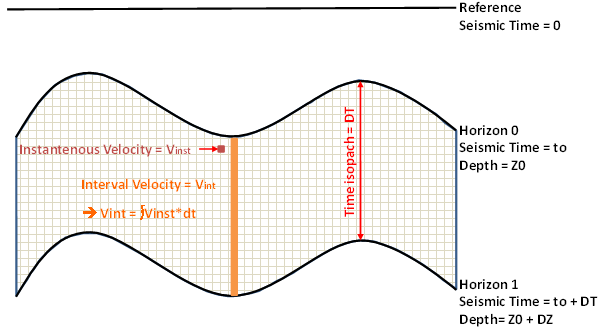
$$
V_{inst} = V0 e^{k \times T}
$$
\( \Rightarrow \) Hypothesis 1: \( Z = Z(t)\)
$$
\Rightarrow V_{inst}(t)=V0 e^{k \times T}
$$
\( Z(t) = \frac{V0}{k} (e^{kt}-1) \quad \) & \( \quad V_{inst} = V0e^{kt} \)
$$
\boldsymbol{
DZ = \int_{t_0}^{t_0+DT} V_{inst}dt = \int_{t_0}^{t_0+DT} V0 \times e^{kt} dt
}
$$
$$
\boldsymbol{
DZ= \frac{V0}{k}e^{kt_0} \times \left( e^{kDT} – 1 \right)
}
$$
$$
\boldsymbol{
V_{int}= \frac{V0}{k \times DT}e^{kt_0} \times \left( e^{kDT} – 1 \right)
}
$$